Welding is an incredibly frequent and important process in manufacturing and repairing of cars, various industrial machines, water, gas and oil pipelines and even stairs, handrails, fences and other home and garden fittings. A skilled welder can join two pieces of metal together and, if done properly, the weld can last for a long, long time. However, if not done properly, several welding defects can occur.
Improper welding can be dangerous and ruin your hard work, not to mention causing breakage, cracking, and other damages in the metals you have welded or holes you have tried to patch. That’s why it’s important for you to get familiar with the different types of welding defects and learn how to avoid them.
Table of Contents
In this post, I will discuss seven of the most common welding defects and how to prevent them! After reading my post, you will be able to identify these imperfections and take corrective action before they cause damage to your product.
Key Takeaways
- Most common welding defects are caused by human error, sub-par performance and negligence. Period. All are preventable!
- You can definitely avoid some welding defects by maintaining a proper environment or preventing you and your equipment from contaminants.
- There are some minor defects that can be detected only by using advanced technology, but most commonly, weld defects are easily detected by a naked eye of the welders and inspectors.
What are Welding Defects?
Welding defects are imperfections or inconsistencies that develop when welding is carried out. Several factors, such as incorrect equipment settings, improper weld preparation, inadequate joint design, incorrect welding technique, and poor quality materials, can cause these defects; there may be a few more invisible factors that I will discuss later in this post.
Welding defects or types of welding defects can range from minor, aesthetic flaws to major structural problems that could compromise your product's integrity, or improper welding may cause harm to you or your family.
For example, some outside steel stairs are welded, and if not welded properly and have a defect, it can lead to an accident. Pipes can burst and cause gas leaks. Cars can breakdown and leave you stranded. Is welding hard to learn? Is that the reason why defects occur? Is it negligence and lack of the commitment to weld properly? Fail to prepare well before you start?
The best way to prevent these welding defects is through careful preparation of the metal being welded, quality control, proper training (resulting in getting a welder certification), and the experience of welders.
7 Most Frequent Welding Defects
Here are seven of the most common welding defects and types of welding defects that you or a welder should be aware of in your work:
1. Weld Crack
This is one of the most common welding defects. Welding cracks occur when weld metal cools too quickly, resulting in a lack of fusion between the two pieces being welded. Cracks can also occur due to poor design and improper preheating or post-welding temperatures.
Poorly designed joint configurations and welding techniques can also contribute to welding cracks. As these cracks weaken the welded joint, they can cause a wide range of issues, such as fatigue or even catastrophic failure of weld metal in extreme cases.
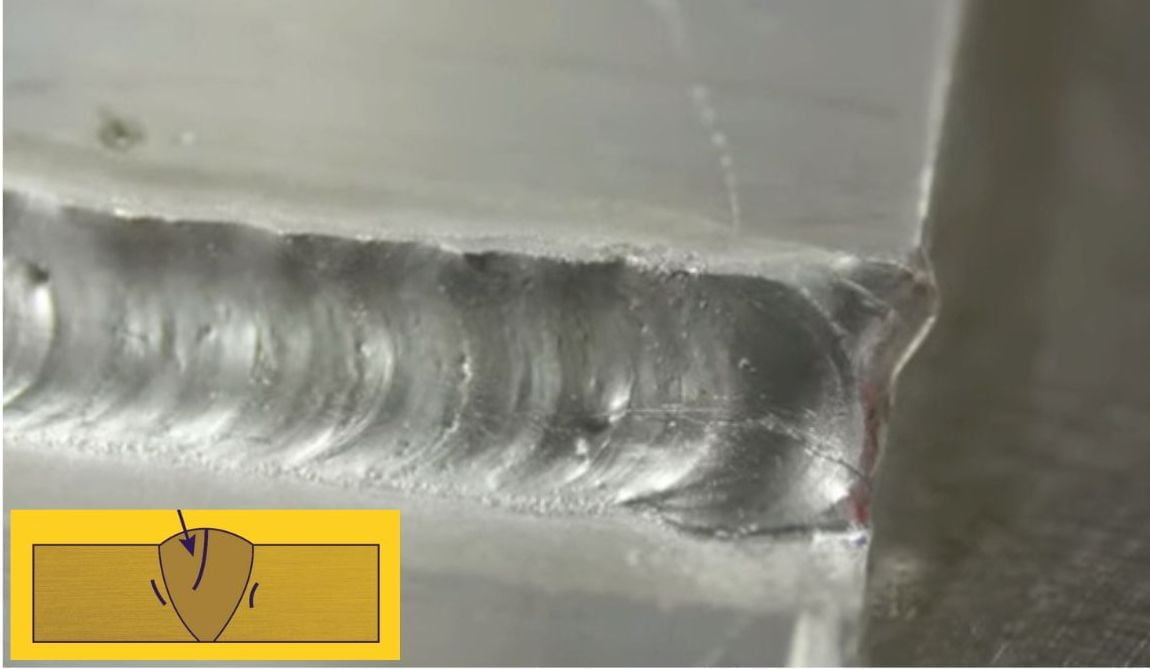

How to prevent a weld crack?
You should watch over proper preheating and post-welding temperatures if they are maintained to prevent a weld crack in the weld metal. Also, it would be best if you used an appropriate welding technique for the best results or to carry out the welding process properly.
If you make a mistake, break your weld and do it again.
2. Incomplete fusion
Incomplete fusion is a welding defect that occurs when two pieces of weld metal are not properly fused. This can lead to cracks, leaks, and other structural problems in the weld joint. Most commonly, incomplete fusion occurs when you input inadequate heat during the welding, which ever welding machine you use, MIG, TIG, Stick, or Flux Core.
This is caused by a low voltage or current setting on the welder, incorrect shielding gas mix, incorrect filler weld metal type, or an improper welding technique. Incomplete fusion can also be caused by contamination in the joint, such as oil, grease, or rust, which prevents the weld from forming a proper bond with the base material.
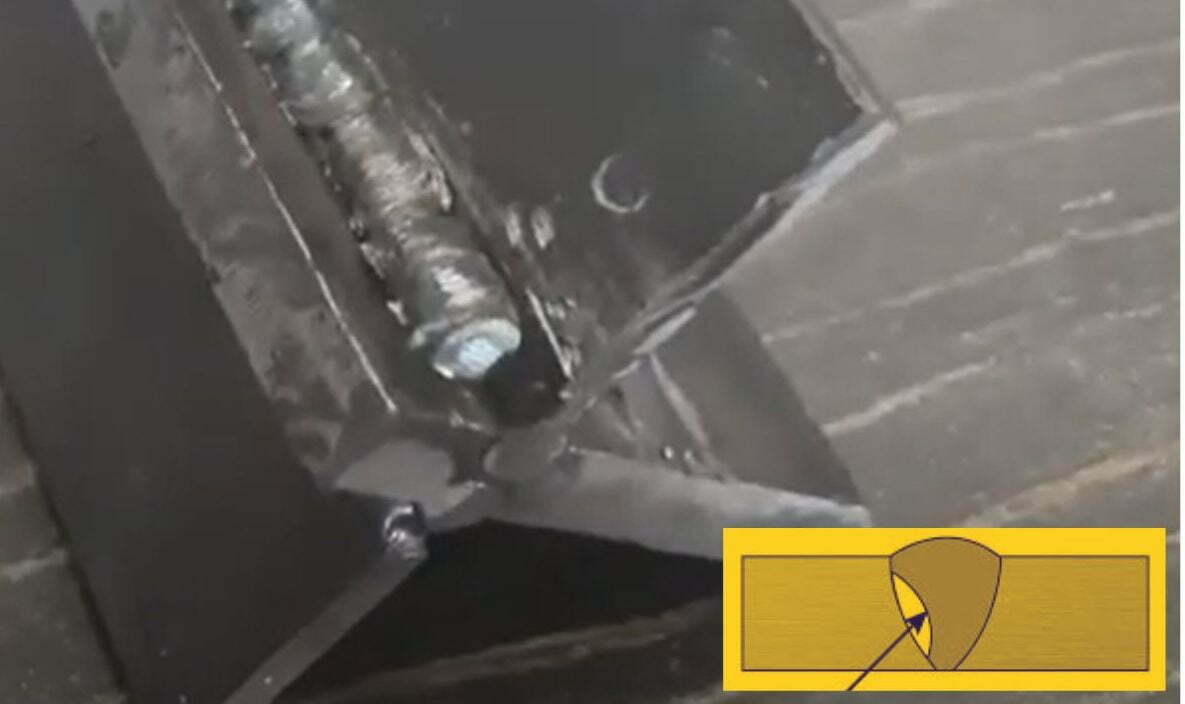

How to prevent incomplete fusion?
You can prevent this defect, to avoid incomplete fusion defects, you should use the correct voltage. I want to point out the current settings on your welder and using a proper technique when welding is mandatory. It is also important to ensure that the welded area is cleaned of any contaminants in an appropriate way before welding begins as it is a basic thing for you or any welder to do.
Welder should also use an appropriate filler metal for the base welding material and joint configuration for metal to be welded is also important.
3. Porosity
This welding defect occurs when some gases, such as hydrogen or nitrogen, become trapped inside the weld material. This can result in tiny holes and cavities in the welded joint, weakening its strength and reducing its fatigue life. This problem is especially common when welding aluminum and magnesium alloys.
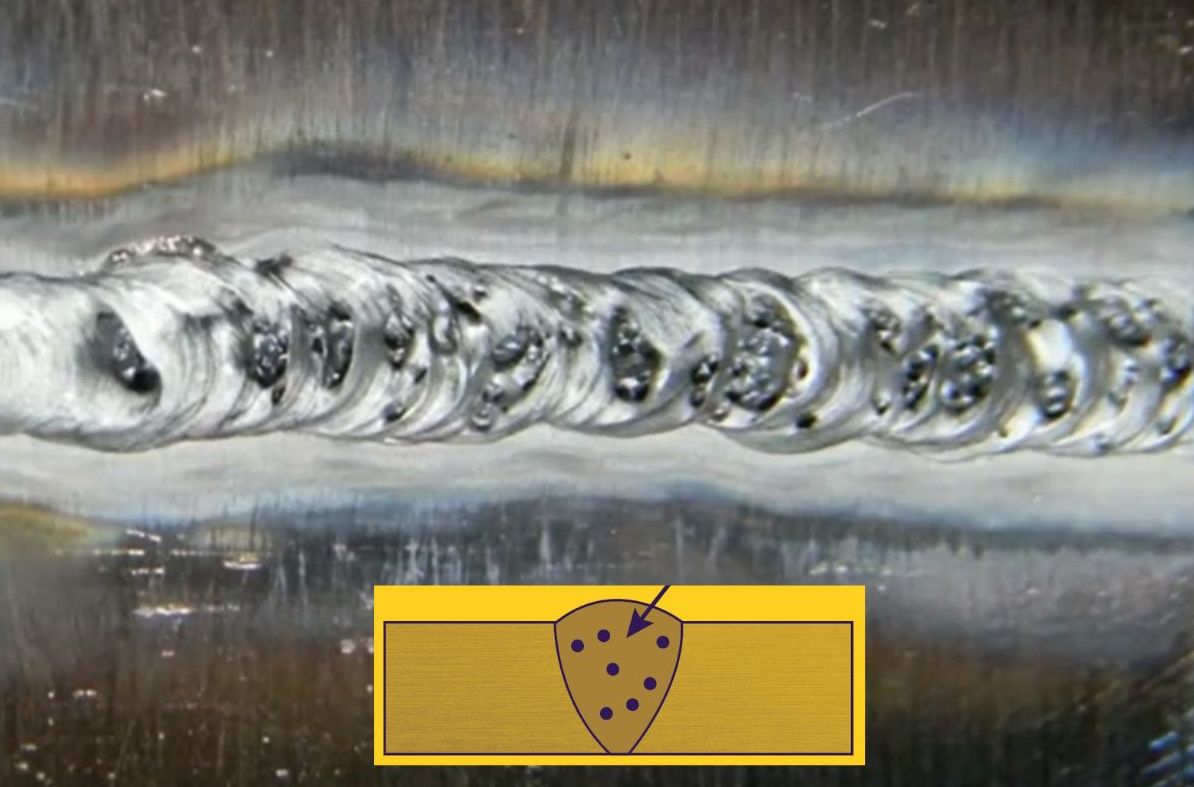

How to prevent porosity?
A welder should use proper techniques, such as reducing the arc size and using shielding gases can be helpful. The welding environment should also be monitored by the welder to ensure that contaminants, such as moisture or oil, do not enter the weld area or even if you are carrying some contaminants as dust. Nowadays Flux-cored wires are used to reduce porosity in some applications.
4. Inclusions
Inclusions are welding defects where foreign materials become trapped in the weld zone during welding. These materials can be anything from slag, oxides, or gas bubbles, which disrupt the normal fusion of base metals or filler materials. Inclusions can lead to porosity, lack of fusion, and cracking, weakening a welded joint's structure and corrosion resistance.
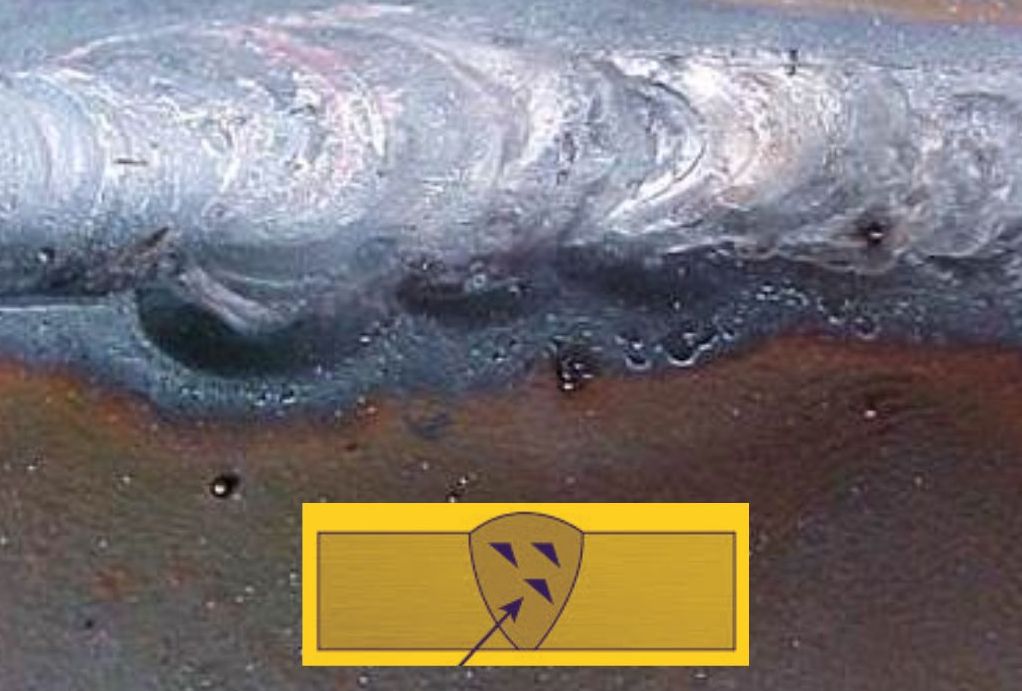

How to prevent inclusions?
It is important to clean the weld area from any foreign material before welding and use proper welding techniques, such as you can keep the electrode angle correct and moving at a steady pace, to reduce the potential for inclusions.
Also, you should adjust the amperage correctly for the thickness of the metal being welded, and check for any contamination that may have occurred during welding. These are proven ways to prevent a weld defect.
5. Mechanical Damage
A welding defect can occur when an external force damages components. This damage can weaken and distort the weld, leading to potential safety issues or product failure. These mechanical damages can happen in several forms, such as unintentional contact during welding, submerged arc welding, mishandling equipment, and parts, or overstressing due to human error.
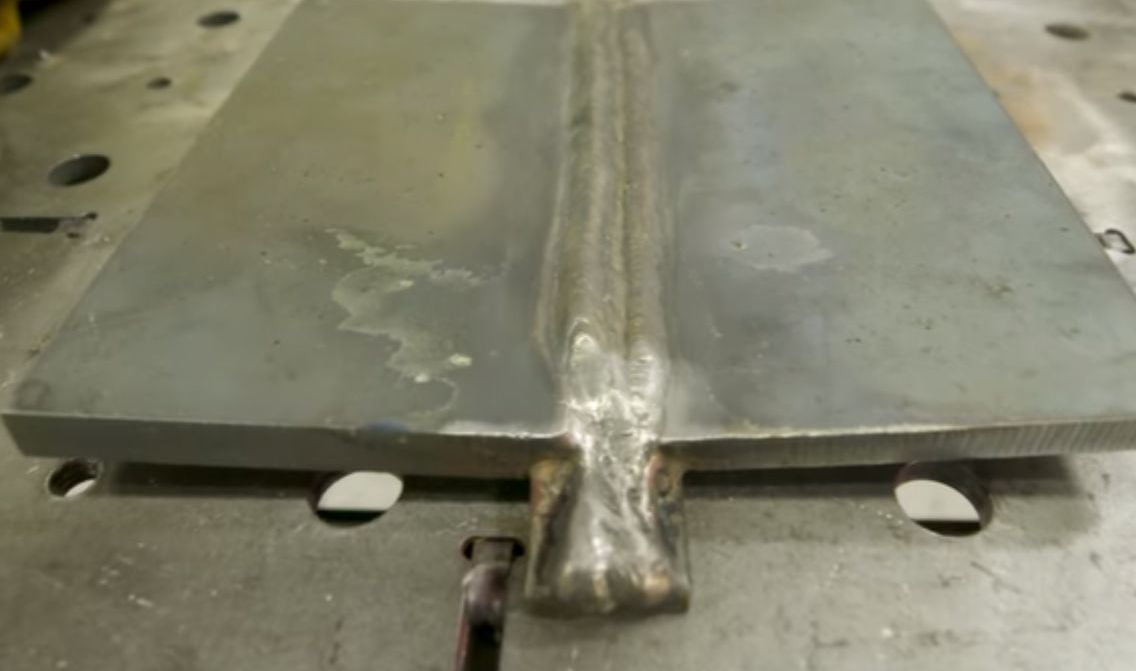

How to prevent mechanical damage?
A welder should make sure that all equipment is handled properly, securely mounted, and free from debris, foreign materials or even any contaminant over the welder before welding begins. Using shields or barriers to guard against excessive heat, sparks, and other hazards as these are also common among welders.
Keeping the area around the welding station clear of any objects that could get in the way or be damaged by stray debris can be a successful strategy.
6. Undercut
The undercut is one of the most common welding defects when the weld metal fails to penetrate completely into the base metal, leaving a groove or crater-like feature in the weld joint. This defect is typically caused by incorrect angles, electrode wire, a cheap weld bead, improper arc length, high travel speeds, and inadequate current.
As this defect reduces the strength of the joint, it is important to ensure that correct welding techniques are used to prevent undercut from occurring.
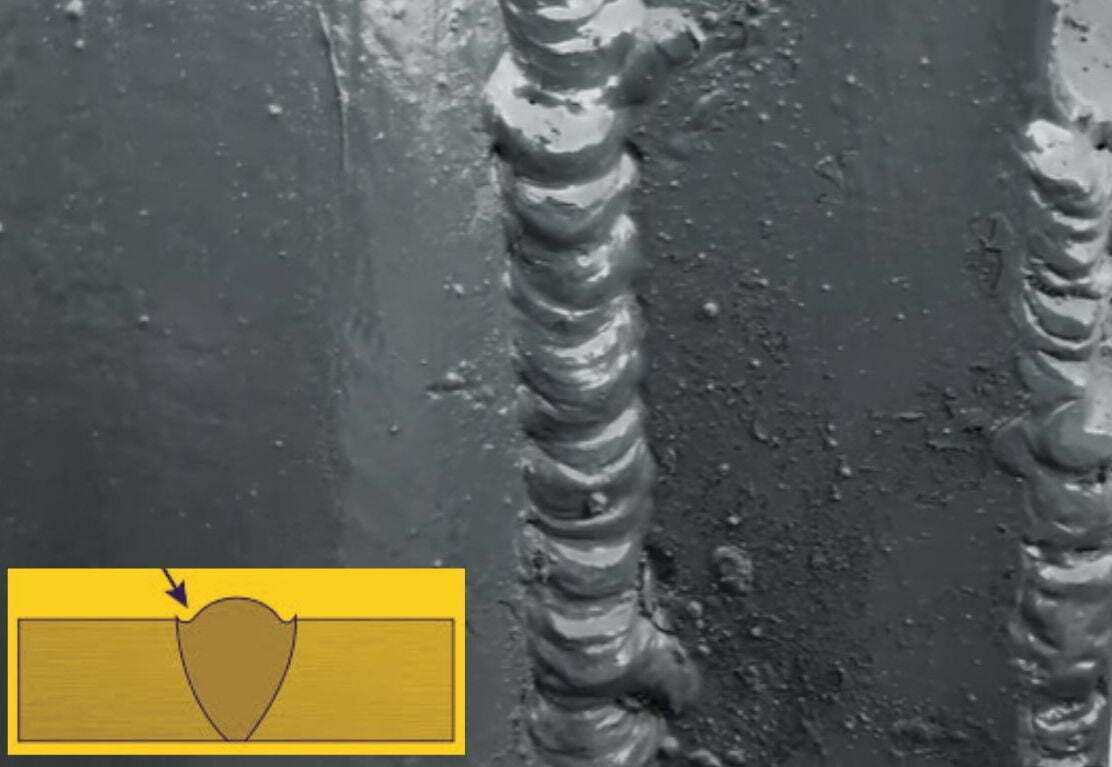
How to prevent Undercut?
Use the correct welding parameters and techniques for the application. It is also important to ensure that the base metal and weld bead is clean and free of contaminants before welding as I have discussed earlier.
Or you can remove the undercut from the weld joint using a grinding wheel or other suitable tools and re-weld it.
7. Spatter
Spatter is a common welding defect when small, molten metal particles are forced out of the weld puddle and onto the surrounding area of the weld surface. This can cause a wide range of issues with molten metal, including poor cosmetic appearance and reduced structural integrity due to penetration gaps or undercuts in the weld.
It can also cause welds to be rejected after visual inspection. Incorrect welding parameters, such as high amperage or improper electrode manipulation, can cause a spatter.
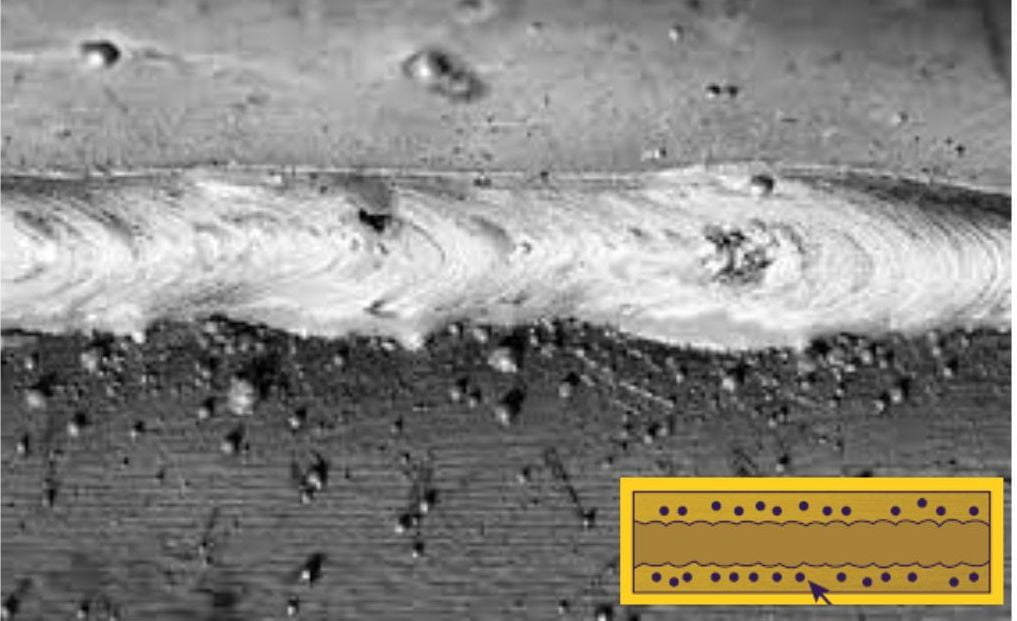

How to Prevent Spatter?
To prevent spatter, make sure your welding equipment is set up properly, use good electrode manipulation and keep arc length in control, correct your welding position, and avoid over-welding. Always wear the proper eye protective gear when welding to protect yourself from any possible sparks or spatter. These are the most frequent causes and remedies for any welding defect.
FAQs Related To Welding Defects
How do you know if there are any welding defects?
There are a few ways to determine if there are any weld defects. Visual inspection is often the most effective way of identifying imperfections, including warping, cracking, and discoloration. Other methods, such as X-ray inspections, ultrasonic testing, and magnetic particle testing, such as weld bead, can also detect internal weld defects or any other types of welding defects that may not be visible to the naked eye.
What are the most common causes of welding defects?
The most common causes of weld defects include improper fit-up, incorrect amperage or voltage settings, inadequate joint preparation, incorrect shielding gas mixtures, improper welding speed, incorrect welding patterns, poor quality of electrode wire, insufficient cleaning of metals before joining, and poor technique that mostly leads to internal welding defects.
In addition to these factors, other materials, such as moisture in the atmosphere, can also lead to a weld defect.
How do you reduce welding defects?
The best way to reduce welding defects is by following proper welding procedures and using the right equipment and proper welding speed. This includes ensuring the joint surfaces are clean, appropriate welding speed, fitting the parts, including the weld pool, properly before welding, selecting the correct amperage or voltage settings for the size of the material being welded, paying close attention to shielding gas mixtures and other welding processes.
Using the right welding techniques is most important, such as keeping the arc length consistent and maintaining a steady speed at the weld surface can prevent external welding defects.

Final Thoughts
Welding is a critical process in manufacturing and construction. Defects can lead to serious accidents, so it's important to be aware of the most common welding defects and how to avoid them. In this blog post, we've outlined 7 of the most frequent welding defects, their causes, and preventive measures.
These seven defects are the most common welding problems that welders and metal fabricators face today. Fortunately, they can all be avoided with extra care and attention. You can prevent costly mistakes by following the proper weld procedure and using the right materials for your project. With a little practice, you'll be able to produce high-quality welds that meet even the most stringent standards.
