Are you a welder who's looking for more information on what is tack welding? If so, then this post is for you! Tack welding is a specialized type of weld used to join metal parts in preparation for stronger, final welds. As you might expect, mastering the technique of tack welding requires understanding its fundamentals and different types. In this blog post, we'll break down the basics of tack welding and explain the various types of tack welds that could fit your project. Read on to get started!
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Tack welding is a specialized type of welding that involves using small welds to hold materials in place before a final weld is applied.
- It is commonly used in construction, automotive repair, and metal fabrication industries.
- Proper techniques and best practices for tack welding include cleaning the metal and adequately fitting the pieces before tacking them, using the correct heat settings based on the thickness of the metal to prevent warping, spacing the tacks evenly, and joining the pieces with the minor filler possible.
What is Tack Welding and How Does it Differ from Traditional Welding?
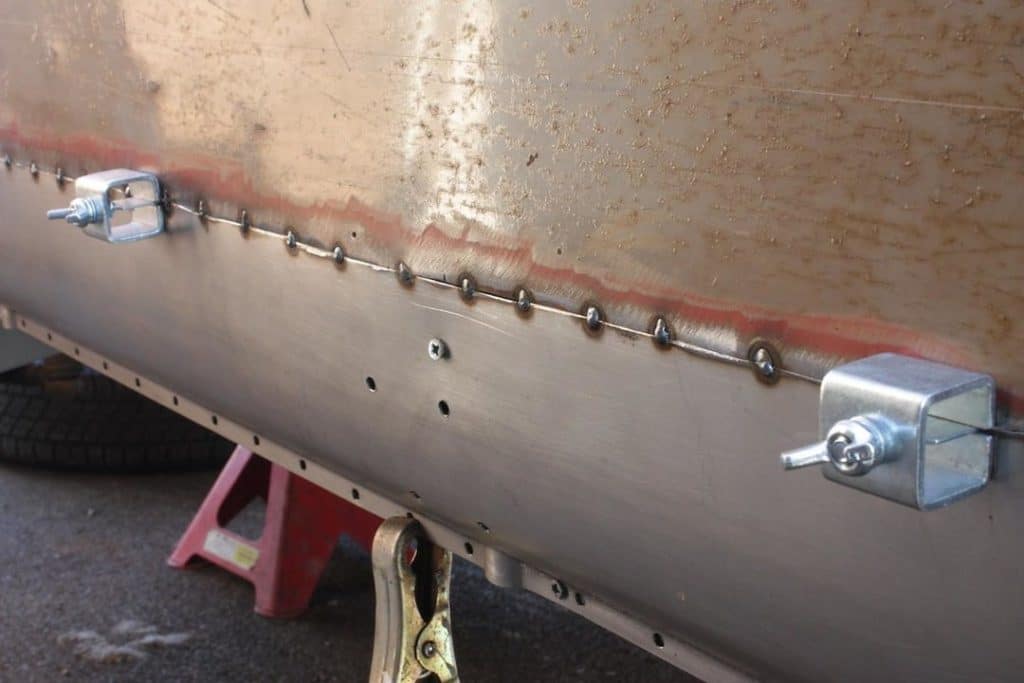
Tack welding is a type of welding that is used to hold pieces of metal together temporarily. It involves using small welds to hold materials in place before a final weld is applied. Tack welding differs from traditional welding because it is not meant to create a permanent bond. Instead, it is used to hold materials in place while the final weld is being applied. Tack welding is commonly used in construction, automotive repair, and metal fabrication industries.
It is an essential technique for ensuring that materials are correctly aligned and fit together before the final welding process. With its ability to create a temporary hold, tack welding is a valuable tool for ensuring quality and precision in welding projects.

The Benefits of Tack Welding
Tack welding is a crucial technique in the welding industry that offers many benefits. It involves using small welds that temporarily hold the two pieces of metal together, allowing the welder to make necessary adjustments before performing a complete weld. The primary benefit of tack welding is that it helps reduce material waste and minimize the amount of rework needed. Tack welding can improve the overall quality of the final weld by ensuring that the metal pieces are held securely in place.
Moreover, tack welding enables welders to work more efficiently, moving the metal pieces around and repositioning them according to their preferences. As a skilled technique, tack welding can save time and effort by minimizing the need for constant start-stop welding.
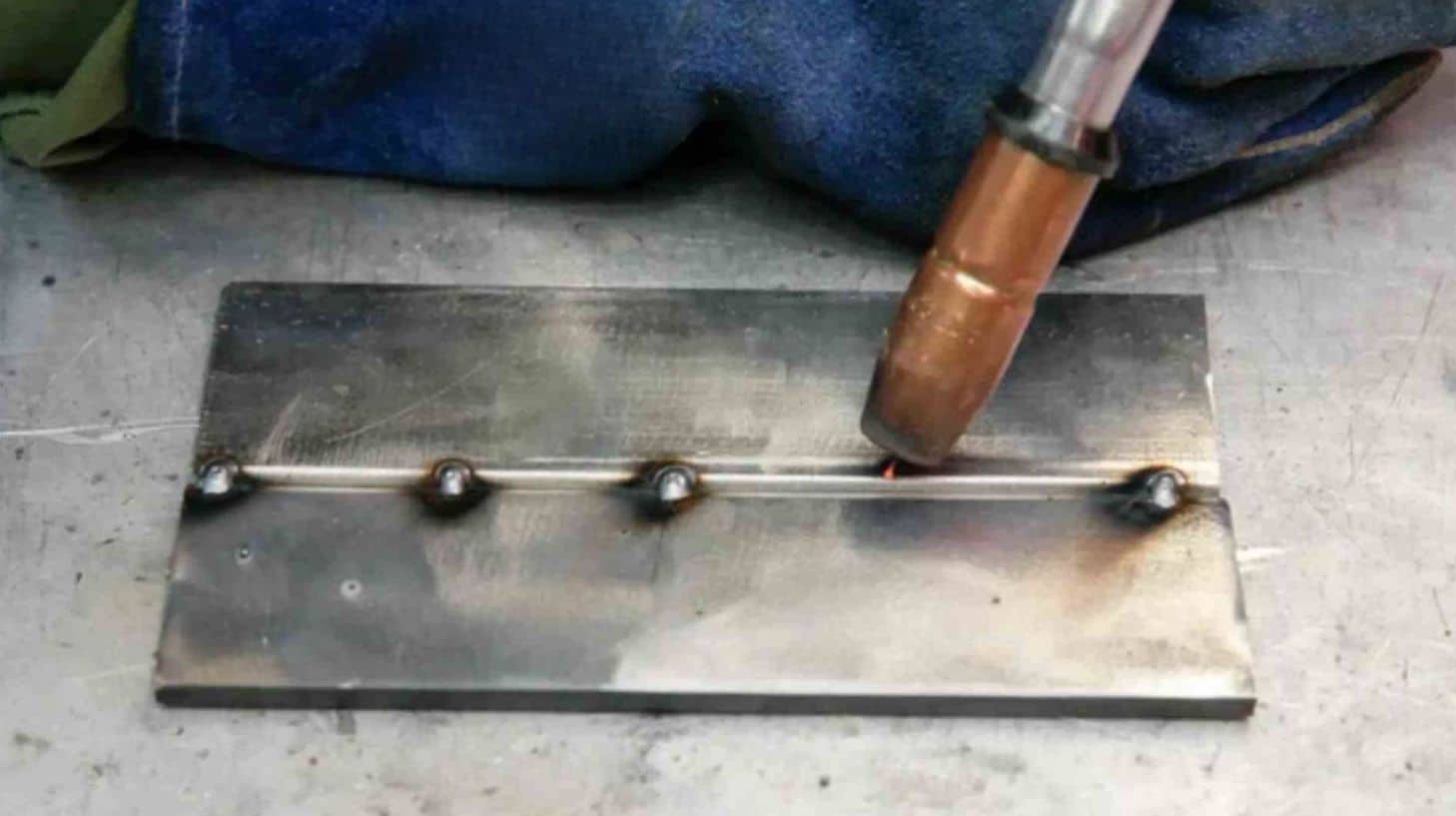
Tack Welding Techniques and Best Practices
Tack welding is an essential part of the welding process and involves joining two pieces of weld together with a series of small, short-term welds. Unlike other types of welding, the tack welding process does not require large amounts of filler material - instead, it relies on precise placement to provide the necessary strength and stability for the finished product. While it has many advantages, tack welding has some disadvantages. Heat build-up can cause the metal to warp, and poor placement of tacks can lead to weak welds that may fail over time.
Proper preparation and technique are critical for achieving a strong weld metal, unlike tack welding. It is important to clean the metal before starting the tacking process, as any dirt or debris can weaken the connection.
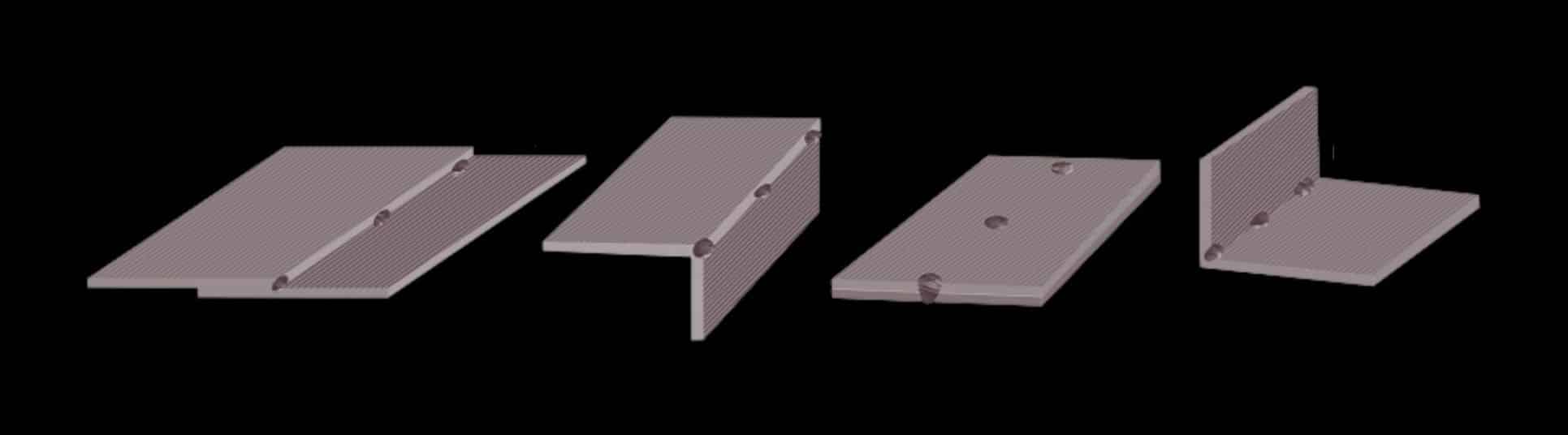
Standard Tools and Materials Used in Tack Welding
Tack welding is a process that temporarily joins two pieces of metal together. It has many advantages, such as the ability to quickly and easily create a weld joint without having to use heat from a traditional welder. However, there are some disadvantages of tack welding that should be considered when deciding whether or not it is the best option for your project.
To create a standard tack weld, you will need the right tools and materials, such as a MIG welding machine or a TIG welder, welding helmet, pliers, wire cutters, welding wire, welding rods, and a grounding clamp. Besides these materials, it is also important to understand how to properly bridge tack welds to achieve the best results.
When using a stick welder to tack weld, I just leave the machine set to what I'm going to use to weld with anyways. I do a small puddle, just enough to hold things in place. If I find those are not big enough to hold, I'll do larger ones, but usually I want the tacks big enough to hold, yet small enough I can still shift the material to push or pull it back to where I want it when it pulls.
With the right tools and materials, tack welding can be an enjoyable and rewarding experience.
Safety Precautions When Working with Tack Welding
Safety should always be the top priority when it comes to tack welding. Unlike TIG welding, which involves a permanent weld between two pieces of metal, this welding process only holds the welded metal in place with a temporary bond. Before beginning any tack welding project, it's crucial to inspect your equipment and ensure that it's in good condition.
You should also wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including a welding mask, gloves, and protective clothing. It's also essential to ensure that your work area is free from flammable materials and adequately ventilated to avoid the risk of fire or inhalation of dangerous fumes while tack-welded components are being worked on. Take breaks as needed and stay alert while working to prevent accidents.
Troubleshooting Tips for Beginners
1. Ensure your work surface is clean and debris-free before you start welding. This will help prevent your welds from being contaminated by dirt or other particles that can weaken the joint or cause porosity in the weld.
2. Ensure that the two pieces of metal you are joining are properly aligned before taking them together. Misalignment of the pieces will lead to an uneven weld and increase the chances of your welding not being successful.
3. Ensure that you have the right tools for the job. Using a tack welder with too high or too low voltage can cause poor-quality welds or damage the equipment.
4. Wear safety gear like gloves and a face shield, when welding.
5. Use clean rods for every weld; dirty or contaminated rods can lead to poor-quality welds.
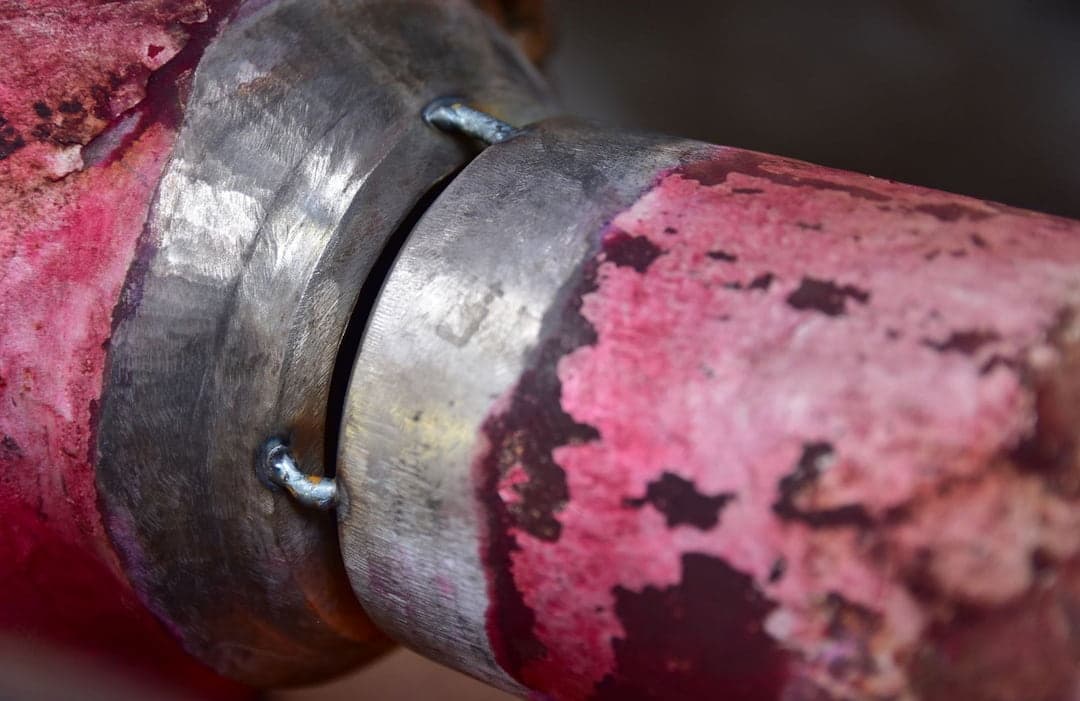

FAQS
What is the purpose of tack welding?
Tack welding is a technique used to temporarily bridge two or more metal pieces together before the final welding process is completed. The standard tack welds are designed to keep the joint gap closed, allowing adjustments to be made before the final weld. This helps ensure the metal pieces are properly aligned and secured before proceeding with the next welding process.
Tack welding is also beneficial in situations where large or complex structures are being welded together, and adjustments need to be made to the position or alignment of the metal pieces. Using tack welding makes welding easier and more efficient while reducing the risk of welding defects such as distortion, warping, or misalignment. The tack welds also provide a secure connection between the two metal pieces, providing extra protection and a strong bond between them before the permanent weld is made. With a successful tack welding process, the final weld can be done with confidence, resulting in a strong, permanent weld that holds the metal pieces together securely.
What are the benefits of tack welding?
The benefits of tack welding include the following:
Holding the pieces in place: Tack welded joints act as temporary welds containing details before a full weld is made. This ensures that the components stay in the correct position during welding.
Easier to make adjustments: With tack welds holding the pieces in place, it's easier to adjust the joint before the final weld.
Increases welding accuracy: Tack welding helps ensure the pieces are lined up correctly before the final weld is made, improving welding accuracy.
Saves time and effort: Tack welding can save time and effort by reducing the rework required if the pieces shift during welding. It also helps to prevent gaps in the final weld, saving time and effort in filling them.
How is tack welding performed?
It is typically performed in the following way:
Preparation: The pieces to be welded are prepared by cleaning and aligning them in the desired position.
Tack placement: Small welds or "tacks" are made at various points along the joint to hold the pieces in place. The tacks are typically spaced several inches apart and placed in a sequence that securely stores the joint.
Checking alignment: After tacks are placed, the alignment of the pieces is checked to ensure they are in the correct position before welding processes with the full weld.
Final welding: Once the pieces are correctly aligned, the final welding starts at one end of the joint and works systematically to the other.
Post-welding: After welding, the joint is inspected, and any necessary finishing work is performed, such as grinding or sanding down rough spots.
