What is stick welding, and why is it trendy among welders? Is it the best path for you to take as a welder? Join in as we go about stick welding also known as Manual Metal Arc Welding (MMAW) and more often as Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW).
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Stick welding is a manual welding process using flux-shielded rods as an electrode.
- One advantage of SMAW is it works well with oxidation or paints on the working surface.
- A disadvantage of SMAW is leaving slag deposits after creating a joint.
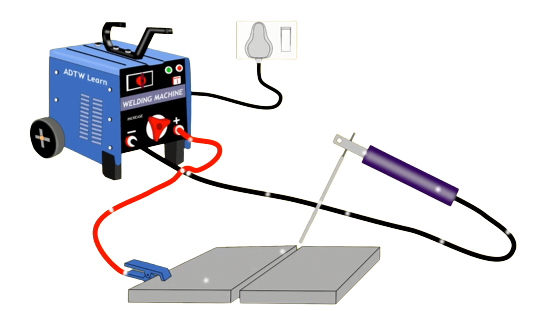
- You only need a stick welder, rod holder, earth cramps, a welding power supply, and standard safety gear.
In this article, we'll define it, show what you need to start stick welding, the safety requirements and then see how to stick-weld. We'll also define electric metal arc welding for the starters.
What is Stick Welding?
Stick Welding is an electric arc welding process that uses flux-shielded welding rods as the welding electrode. It's also called Manual Arc Welding or (SMAW) Shielded Metal Arc Welding.
The flux on the surface of the electrode is a combination of metal powders, composites, and a binding agent. Its purpose is to shield the weld pool during the procedure to produce firm and stable joints.
This process uses direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC) and an anode for welding. Using DC or AC to produce an electric arc depends on the electrode for the specific weld process. So, if you're using larger electrodes, you'll require higher currents for higher deposition.
What Is Stick Metal Welding Used for?
Stick welding is a typical welding process in joining metals in almost all arc welding operations. The reason it's trendy is its simplicity and versatility. It utilizes different rod types and sizes, and it's also adaptable to many welding positions and applications.
But stick welding is handy and popular with heavy-duty works that involve steel and iron. Other hard metals that use stick welding are nickel & nickel alloys and high alloy steel. Welding aluminum with a stick welder is also possible.
Welders use SMAW widely in maintenance and repair companies. The construction of heavy-steel structures also uses this method. Heavy-steel structures include pipelines, underwater welds (worth mentioning how dangerous underwater welding is), shipbuilding, farm machinery, and others.
What Do You Need To Start A Welding With SMAW?
To weld with SMAW, you need the following stick welding equipment.
- A flux-shielded arc welding electrode
- A rod holder
- A continuous voltage or a Stick welder
- Earth clamp
You must also have the basic welding apparatus that includes:
- Welding magnets help with maneuvering the welding angle. A framing jig also helps with making easy 90-degree angles.
- Welding clamps to hold your project together
- A file to remove finished metal burrs
Now you have the base metal, electrode holder, welding filler metal, and metal workpiece, and you're all set. How do you stick weld? Before that, here are the safety needs.

Stick Welding Safety Needs
The produced welding fumes are poisonous. You, therefore, need to arm yourself with personal protective equipment and clothes that include the following.
- Leather welding gloves to safeguard your hands.
- The welding helmet with proper auto-shading properties for the eyes
- A long-sleeved non-flammable shirt/welding jacket and non-flammable trousers
- Fireproof boots
- And a fire extinguisher
Also, be aware of the flash from Ultra-Violet light produced by the welder. It causes sunburn-like burns on the skin or any unprotected surface. If it flashes into the eyes, it feels like sand entering the eyes.
Avoid welding near flammable materials. It may cause tears or explosions. Reading the warning labels in gear and sticking to what they say is safer.
How Do You Perform Manual Metal Arc Welding?
In stick, an electric current flows through the metallic electrode, forming an electric welding arc between the metal workpiece and the electrode.
Then, the metal piece & the electrode melt, forming the weld pool, a combination of molten metal from the electrode and base metals. It's interesting to learn how to use a spot welder to utilize a completely different process with no consumable electrodes and no shielding gas.
You've seen a lot of names for this process, and there's another. It comes from the action of the electrode. Because the electrode continuously melts away to become part of the welded structure, it's called a consumable electrode. Hence, the process is also called the consumable electrode process. We also explained the meaning of numbers on welding rods in detail.
The flux coating shields the process from contaminants by producing a protective shielding gas to safeguard the weld when heated.
Advantages of SMAW
The advantages of this welding include the following.
- The ground clamp works well while grasping the filler material further from the weld joint.
- It's versatile. Hence, replacing and changing rods makes welding metals like stainless steel and many others possible.
- Ideal for outdoor and indoor welding processes because of a longer arc length.
- Using direct electric current helps me adjust the electrode rods' polarity, lessening the chances of burn while welding thin materials.
- It does not require shielding gases like metal inert gas welding or flux-cored electrodes like in flux-cored arc welding techniques.
Disadvantages of Stick Metal Welding
Before repainting or doing a consequent weld, ensure you chip the slag away or scratch it off using a file. Other cons of SMAW include the following.
- The spatter produced using direct current is less and only welds thinner metals, unlike AC which welds ferrous metals. It's only possible to weld metal thicker than 1/8 inch.
- Also, there's an interruption in the welding procedure, as you must keep changing the welding rod.
- Stick metal welding is also called the manual arc welding process because stick welders consider it manual, making it hard to mechanize.
- Oxygen contaminations limit its application to reactive metals like columbium, titanium, and zirconium.
What Is Arc Welding?
Arc Welding entails the process of welding that employs an electric welding arc that creates enough heat that melts and joins metals. You want a power supply to create the electric welding arc between the non-consumable or consumable electrodes. You have alternating or direct electric current for the power supply.

Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Types of Arc Welding?
The four Arc Welding methods include the following.
- Stick welding, also called Shielded Metal Welding
- TIG (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding)
- Then Flux-Core Arc Welding.
- MIG welding (Metal Inert Gas Welding)
Is Stick Welding TIG or MIG?
No, stick welding is not TIG or MIG. MIG uses gases for shielding the weld, while Stick is self-shielded. TIG welding uses a non-consumable electrode, while stick uses a consumable one.
What is Better, Stick or MIG Welding?
Stick welding produces stronger welds because of the better penetration of thicker materials. On the other hand, MIG also offers averagely good welds with medium thickness, but it's less effective than Stick. MIG is better than stick for welding thinner materials.
Why Is It Called Stick Welding?
SMAW is called stick welding because of its electrode. The rod takes the shape of a stick. It can weld many metals.
