What is reverse polarity in welding? Well, the concept of reverse polarity may seem complicated at first glance, but understanding the basic principles of this process can improve your welding results, speed up welding operations and help maintain the integrity of all metals being welded.
Table of Contents
In this post, we'll look in-depth at reverse polarity and how it works during a weld. Whether you're new to welding or need a refresher on this important technique, read on to learn more!
Key Takeaways
- In simple words changing the direction of electric current while running through the arc welder is called polarity. It is an important process to make joints stronger and much more.
- Normal AC or DC welding does not have that much effect; rather this process comes in handy and a welder can use this for the ideal joining of thicker materials.
Reverse Polarity
Reverse polarity is a welding technique that changes the direction of the electric current when running through an arc welder. By reversing the electrical current, welders can achieve a different type of metal fusion with improved quality and greater speed.
This change in the electric current affects how metals bond and fuse together during a weld, allowing for more precise control over the welding process.
This polarity is typically used with MIG (metal inert gas) welding machines, the most commonly used welders today. It's also known as GMAW (gas metal arc welding), which creates an electric arc between a wire electrode and the surface of the metal being welded. The arc welds the metals together and the wire electrode melts to form a strong bond.
When using this polarity, the electric current flows in the opposite direction than it would typically when welding with direct polarity. This reverses the flow of electrons between the fused metals creating a stronger fusion without needing a filler metal.
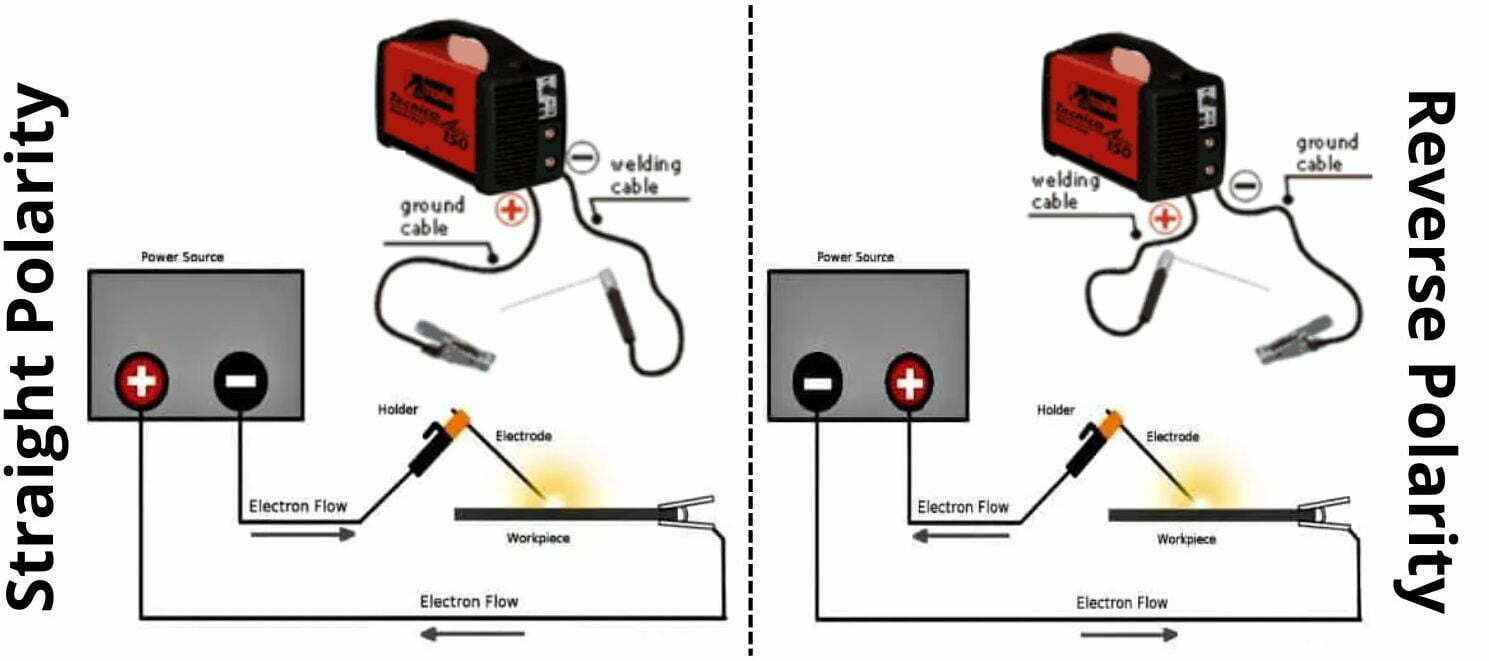
Why Is Reverse Polarity Important?
Polarity is important for several reasons. The main benefit of using this polarity is that it allows welders to create stronger bonds without needing additional materials. This reduces costs, improves overall welding speed, and provides superior-quality results.
By reversing the electric current flow, welders can also more easily control the strength and depth of the weld, allowing for greater precision when working with various metals.
For instance, this polarity is often used when welding thicker plates and materials that require a strong bond. Due to the increased temperature created by this technique, it can create a stronger bond than direct polarity in these cases.
It's also commonly used when welding aluminum and stainless steel, allowing welders to easily control the arc's shape.
This polarity is also beneficial when working with thinner metals as it produces less splatter and provides a cleaner finish than direct polarity. This reduces cleanup time and improves safety, as less debris is created when welding with this technique.
When Should You Use Reverse Polarity Welding?
You can use this polarity welding when you need a stronger weld joint than normal AC or DC welding can provide. This method is also ideal for joining thicker materials such as steel and aluminum.
Due to the deep penetration of this polarity arc; this technique is often used when good access to the back side of the material is unavailable. This is beneficial for making welds in restricted spaces or on workpieces that are difficult to turn over.
It is also popular because it has a higher deposition rate than an AC arc meaning faster travel speeds and less spatter during welding. It can also be used with shorter arcs, which is much easier to control than other welding methods.
What are the different types of polarity in welding?
Polarity in welding is the direction of the electric current used to create an arc. There are two types of polarity: direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC).
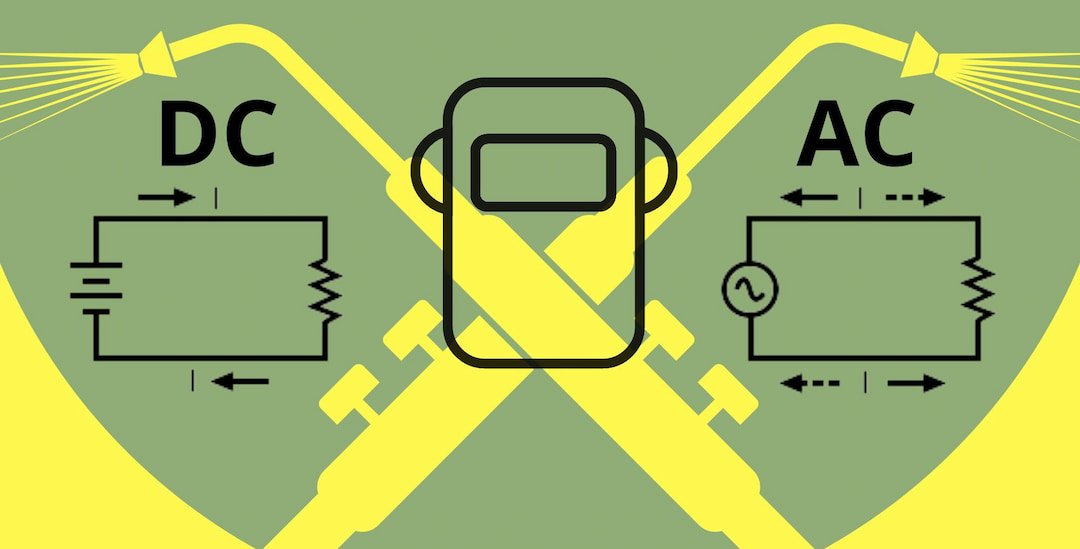
Direct Current Reverse Polarity: DC reverse polarity uses an electrode made of a metal such as steel or titanium. This electrode type allows the current to travel in one direction and produces a more focused weld. This type of polarity also produces less spatter creating a cleaner weld.
Alternating Current Polarity: AC welding uses an electrode made of copper or aluminum. This electrode type allows the current to change directions, producing a wider and shallower weld.
Main Differences Between Reverse and Straight Polarity in Welding
The difference between straight and reverse polarity in welding lies mainly in how the electricity flows through the arc. In this polarity, the electrode is connected to a positive pole of the power source while the workpiece is connected to the negative pole.
This allows for a more efficient transfer of heat from the electrode to the workpiece, which helps create stronger welds and saves from wrong polarity.
In straight polarity or direct current straight polarity, the electrode is connected to the negative pole of the power source while the workpiece is connected to the positive terminal of straight polarity.
Straight polarity allows for an even spread of heat throughout the weld, which helps with providing more uniformity in your welds. These are the differences that can make you define straight and reverse polarity.
How Does Polarity Affect Arc Welding Performance?
Polarity plays a major role in arc welding and can greatly affect performance. In direct current (DC straight polarity) welding, the electric current is passed from the electrode tip to the workpiece, creating an electrical arc between them.
The polarity of this current determines which material will be melted and removed during welding—the anode or cathode as with straight polarity. If the wrong polarity is used, the arc will not be as effective, and weld quality may suffer resulting in a short electrical circuit.
The application of alternating current polarity welding also requires understanding the correct polarities to achieve desired results. In this type of welding, two alternating current waves are used to form the welding arc. The electrode is the anode of one wave and the cathode of the other, resulting in a more balanced heat distribution.
FAQs Related to What is Reverse Polarity in Welding
Why is DCEP called reverse polarity?
DCEP (Direct Current Electrode Positive) is called reversing polarity because current flows from the electrode to the workpiece when welding. This is the opposite of the standard alternating current polarity welding process where the current flows from the workpiece to the electrode.
Can reverse polarity damage your welding machine?
Yes, polarity can cause damage to your welding machine, as it has the potential to send too much current through the weld. This can cause excessive heat buildup, leading to component failure or fire. Improper use of this polarity may produce weak welds with low penetration and poor fusion.
Why would you use reverse polarity on a welder?
Reversing polarity on a welder can make several welding processes more efficient and help produce better welds.
For example, when welding aluminum or magnesium it is often necessary to use this constant polarity to create a stronger bond between the two pieces being joined. When welding steel with an arc process; this polarity causes the arc to be more stable, resulting in a stronger and more reliable weld.
Final Thoughts on Reverse Polarity in Welding
In conclusion, reverse polarity welding is an important process that welders often use to join two pieces of metal together. A welder must understand and use the constant polarity connection to obtain a satisfactory and safe result from the welding arc.
We hope that you have a better idea regarding what this polarity is in welding, why this technique is important, and some key differences between straight and reverse polarity welders.
