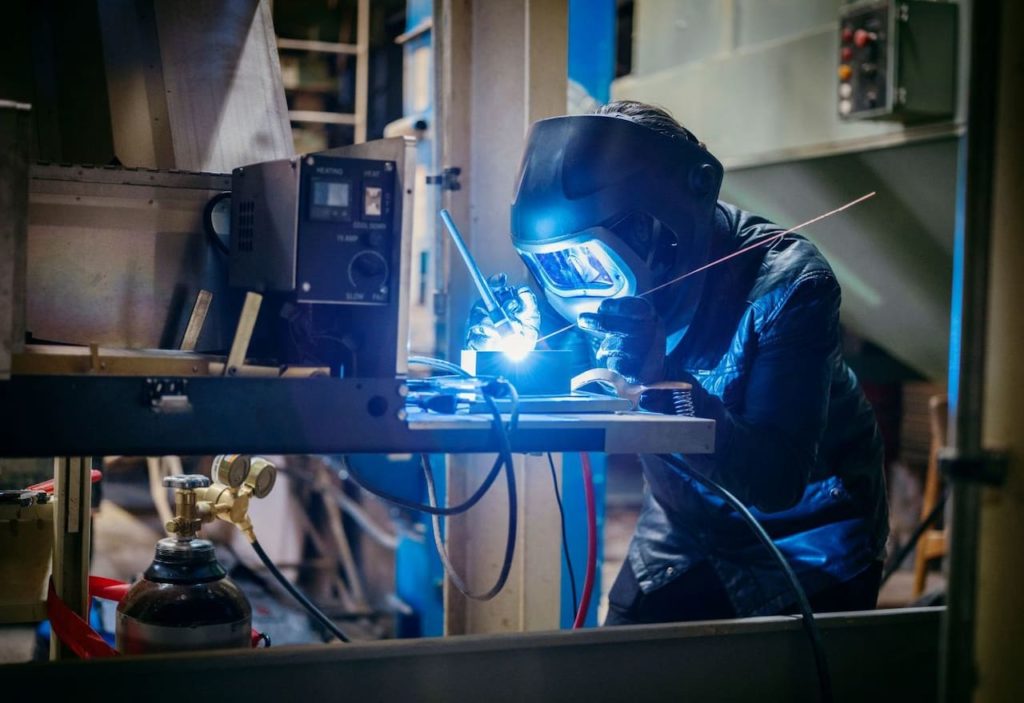
Welding is a complex process that requires precise, optimal gas flow rate control to achieve optimal results. In TIG welding machines, the right type and blend of gases protect the metal from oxidation and corrosion during the welding process.
Table of Contents
Finding the perfect combination of TIG Welding Gases can be complicated and overwhelming, but with just a few simple steps, you can learn the types best suited for your project.
Knowing which type suits a particular welding process will help you achieve the best results. Different gases have different properties when exposed to heat and pressure.
What Gas Is Best For TIG Welding?
TIG Welding With Argon
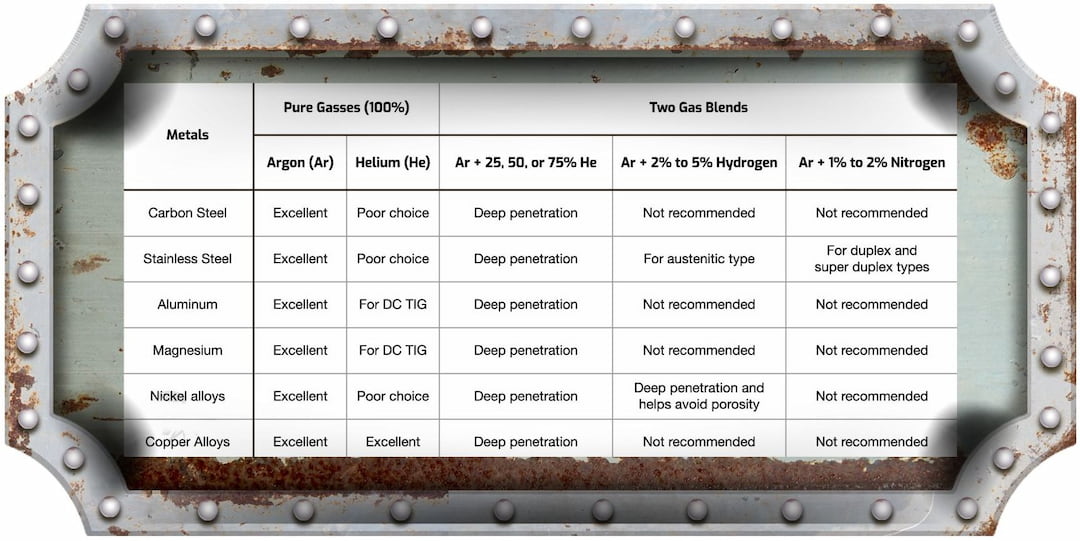
The most common gas for TIG welding is Argon. It’s an inert, colorless, odorless gas that provides a more stable than arc welding, and shields the weld from oxidation during welding. It's used in almost all Tig Welding applications since it produces clean results and can be used with various materials.
A mixture of Argon and Helium (Ar/He) is often used for stainless steel welding. This combination provides greater penetration into weld metal than pure Argon, resulting in deeper welds and stronger joints.
For aluminum welding, a blend of Argon and Hydrogen (Ar/H2) is recommended because it avoids the introduction of oxygen into the weld and helps to reduce porosity. Specialized aluminum Tig welding applications may blend Argon, Helium, and Hydrogen (Ar/He/H2).
Regarding TIG Welding, the most important factor is finding the right combination of gases for your project. Different metals require different mixtures to produce strong and clean tig welds.
TIG Welding With Helium
Helium is a noble gas that’s often used in combination with Argon for Tig welding. While it provides many of the same benefits as pure Argon, Helium has some unique characteristics that make it an ideal choice for certain welding applications.
For example, when combined with Argon (Ar/He), Helium produces a hotter arc with more penetration than pure Argon. This enables it to weld thicker and harder metals and alloys like stainless steel and aluminum. It also helps create stronger joints with deeper penetration on difficult-to-weld metals.
In addition, Helium has a higher thermal conductivity than Argon, making welding faster and more efficient. It also helps create a tighter and cleaner weld bead with improved metallurgical properties, making it ideal for precise welding applications. Tig welding with Helium is not the best choice for all metals because of its cost and complexity. In addition, some metals may be sensitive to contamination from the helium, so proper shielding should be used.

TIG Welding With Hydrogen
TIG welding with Hydrogen is often recommended for aluminum welding applications. Hydrogen helps reduce porosity and saturation, resulting in a better weld joint. It also assists in creating an even welding arc and reduces oxidation during welding.
Combined with Argon (Ar/H2), it produces a smaller arc providing greater control over the weld. It also helps to reduce arc spatter and increases arc travel and arc welding speed together, resulting in faster welding times. A mixture of Argon, Helium, and Hydrogen (Ar/He/H2) is often recommended for aluminum welding since it provides better control over heat input by reducing distortion and preventing excessive metal heating.
These blends also help reduce contamination and produce more consistent welds. Hydrogen can also be used for stainless steel and other metal welding applications, though it’s not as commonly used due to its cost and complexity.
When using TIG welding with Hydrogen, special attention must be taken to the welding parameters to ensure proper shielding, or else the hydrogen could cause weld contamination. TIG welding with Hydrogen can produce strong, clean welds when used correctly.
TIG Welding Shielding Gas Blends
TIG welding shielding gas blends protect the weld zone from contamination and oxidation during welding processes. The right blend of gases can improve welding performance regarding weld quality, joint strength, penetration depth gas flow rate, and overall efficiency.
A combination of Argon (Ar), Helium (He), and Hydrogen (H2) is the most commonly used shielding gas for TIG welding applications. Argon is an inert gas that provides a more stable arc, and shields molten metal in the weld from oxidation. Helium has a higher thermal conductivity than Argon, making welding faster and more efficient. It also helps create a tighter, cleaner weld bead with improved metallurgical properties.
Specialized aluminum Tig welding applications may also require the addition of Helium (Ar/He/H2). A blend of Argon, Helium, and Hydrogen may be recommended for stainless steel and other metal welding applications.
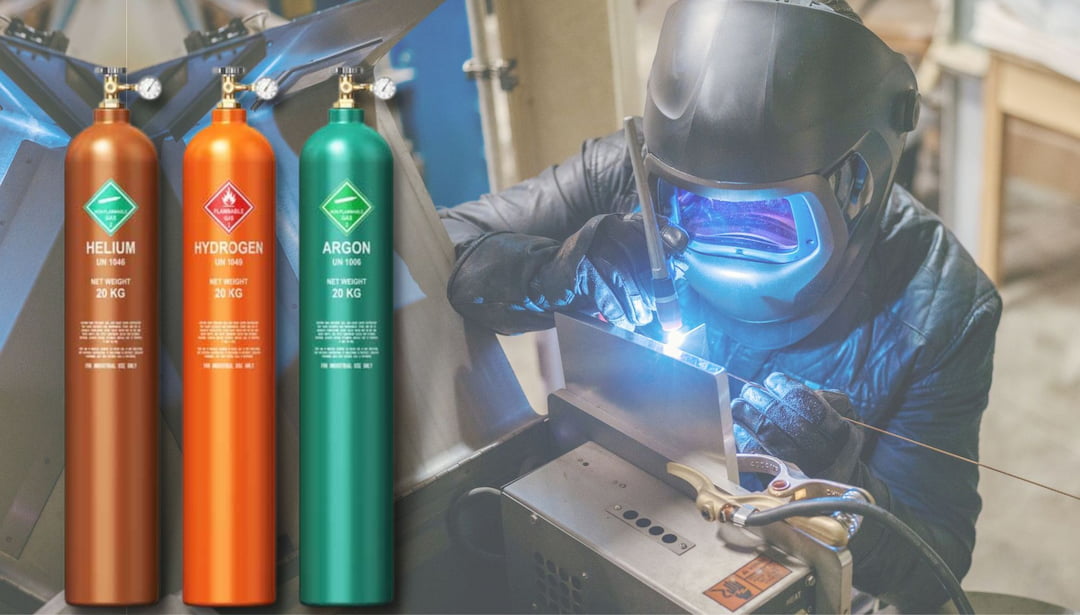

How to Choose the Best Welding Gas for TIG Welding
Choosing the right welding gas for TIG welding can be difficult, as many factors must be considered. It is important to know the type of metal you are working with and what will be the most effective tig shielding gas to produce a strong and high-quality tig welders.
When choosing a welding gas for TIG welding, it is important to consider the type of metal you are working with. Different metals require different mixtures of shielding gases to achieve optimal results.
For example, aluminum usually requires a blend of Argon and Hydrogen (Ar/H2), and specialized aluminum Tig welding applications may also require the addition of Helium (Ar/He/H2).
A blend of Argon, Helium, and Hydrogen may be recommended for stainless steel and other metal welding applications. It is also important to consider the cost and complexity of the gas used for TIG welding. Helium has unique characteristics that make it an ideal choice for certain welding applications, but it can be costly and difficult to work with. Similarly, Hydrogen is recommended for aluminum welding applications but can be costly and complex.
Additional Features of TIG Welding Gas
TIG welding gas is essential for the successful completion of any welding project. Beyond the basic shielding gases of Argon, Helium, and Hydrogen, additional features can be beneficial when selecting a TIG welding gas.
For increased safety and accuracy, some welders opt for blends that contain Carbon Dioxide (CO2). This gas helps reduce the arc's temperature, making it easier to control and reducing the risk of accidents or contamination. It also increases welding speed and improves weld penetration, which can improve joint strength and quality. Nitrogen (N2) is often added as a TIG welding gas for stainless steel applications.
This gas helps create stronger welds and improves the metallurgical properties of molten weld pool the two producing welds and joint. It also helps to reduce spatter, resulting in faster welding times. An Oxygen/Argon (O2/Ar) mix is often recommended for aluminum arc welding in applications. This blend prevents oxidation from occurring during the arc welding process and creates a stronger weld with better penetration depth.
An insufficient mixture of shielding gases may also cause arc blow-out, which can be dangerous. The right TIG welding gas is essential to achieving strong, high-quality welds. Different metals may require different mixtures of shielding gas, and additional features such as CO2, Nitrogen, or Oxygen can improve safety and accuracy during welding processes.
FAQs
What are the benefits of using tig welding gas?
The benefits of using tig welding gas are improved weld quality, increased joint strength, deeper penetration depths, more weld penetration profile reduced distortion and contamination, improved efficiency, and faster welding times. Additionally, using the right blend of gases for specific metals can help ensure optimal results.
What is the best shielding gas for TIG welding?
TIG (tungsten inert gas) welding is one of modern metal fabrication's most versatile and commonly used techniques. The right shielding gas must be selected for different metals to ensure a quality TIG weld. Generally, pure argon shielding gas is often used as a shielding gas for TIG welding because it produces strong welds with minimal spatter and good penetration. Argon also reduces the risk of oxidation, which helps to ensure a clean weld with maximum strength. Other shielding gases, such as helium and oxygen, can also be used with TIG welding, but pure argon is usually the preferred gas for most applications. When selecting the right shielding gas for a TIG welder, it is important to consider the type of metal being welded.
How do I store and handle TIG welding gas?
Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) is a popular welding process that uses an electric arc to create localized heat at the point of contact between a filler wire and two pieces of metal being joined together. In order to avoid oxidation or burning of the weld, an inert shielding gas is used to protect the hot metals from atmospheric gases such as oxygen and water vapor. The proper storage and handling of the shielding gas is essential for ensuring a successful weld.
When storing and handling TIG welding gas, it is important to take steps to ensure that the purity of the gas is not compromised. This includes properly sealing containers and preventing moisture from entering them. It's also important to keep cylinders away from heat sources and store them in an upright position.
How can I troubleshoot tig welding gas issues?
If you are experiencing issues with tig welding, it is important to first identify the cause of the issue. Common causes of mig welding tig out include incorrect shielding gas mixtures, inadequate gas flow rates or through rates, and improper usage or handling of the cylinders.
